Properties of aromatic molecules on 2-dimensional carbon material
I am now doing theoretical investigation on properties of aromatic molecules adsorbed on graphene, well-known 2-dimensional carbon material, by implementing theoretical simulation based on quantum mechanics.
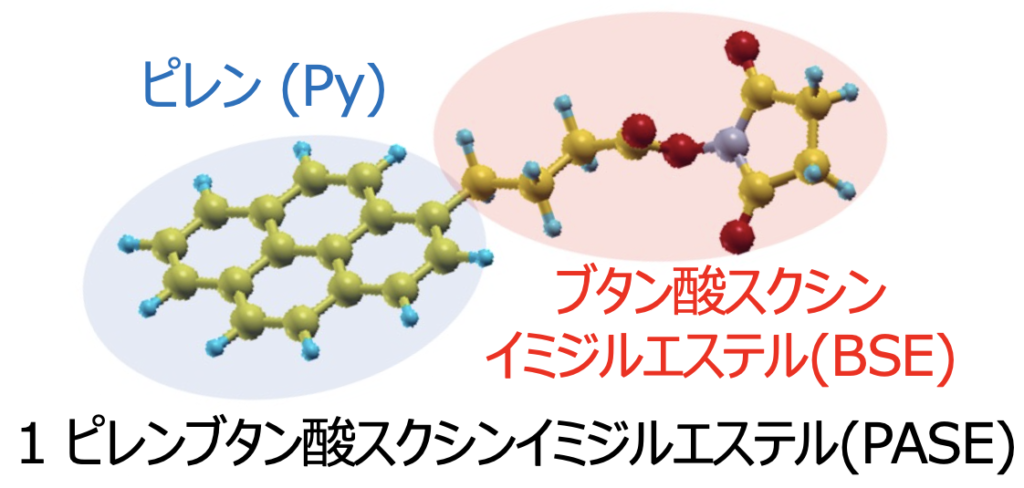
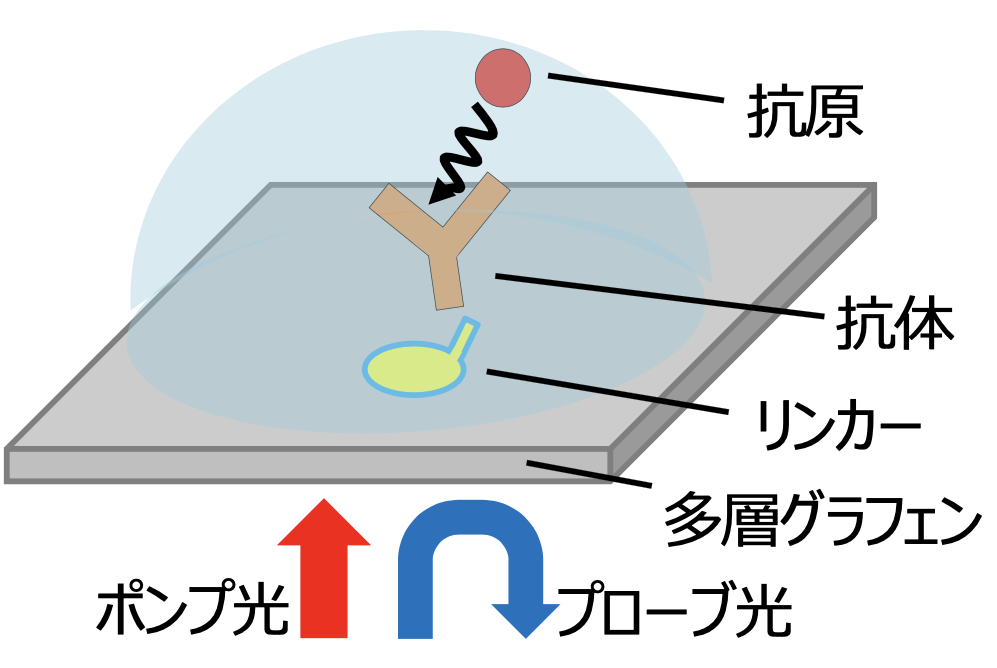
It is well-known that aromatic molecules have high affinity with graphene due to the van-der-Waals interaction. Of all aromatic molecules, those having functional that forms covalent bond with amino-acid, which is the component of protein, are expected to be applied for biosensing-device detecting biomaterials like viruses. Those molecules are called linker, which connects between carbon material and protein. The properties of linker is actually related to the functionality of biosensing-device. Therefore, elucidating the behavior of linker on graphene plays a crucial role in the application for sensor device.
However, the direct observation of linker molecules on graphene by experiment is not easy. In my research, I make use of sophisticated computer simulation and predict the physical and chemical properties that linkers have.
I found that properties of linker molecule will change depending on external environment surrounding linker, such as in solution and under vacuum condition. Consequently, the design of operating environment for improving functionality of biosensing-device was indicated to be possible.